Tracking a Freshwater Invader across New York and New England
Posted in Interesting Plant Stories on June 23, 2015 by Robin Sleith
Robin Sleith, a Ph.D. candidate in the Commodore Matthew Perry Graduate Studies Program at The New York Botanical Garden, is researching algae under the direction of Kenneth G. Karol, Ph.D., Associate Curator in the Cullman Program for Molecular Systematics and the Botanical Garden’s specialist in algae.
Credit: Robin Sleith

Credit: Robin Sleith
This summer, a team from The New York Botanical Garden will set out for the second year to document the diversity of green algae that live in hundreds of lakes in the northeastern United States and determine the distribution of an invasive freshwater alga species, Nitellopsis obtusa, or starry stonewort.
Starry stonewort, which is native to Europe and western Asia, is replacing native plant species and threatening the habitat and food sources of small fish and invertebrates in the lakes where it is found. Growing to a height of seven feet in water as deep as 30 feet, starry stonewort forms dense mats that out-compete native species.
First discovered in the St. Lawrence Seaway in 1978, it has spread at an alarming rate through the Great Lakes and into inland lakes in New York State. It is easily transported from lake to lake as plant debris caught in boat trailers.

Credit: Robert Stewart.
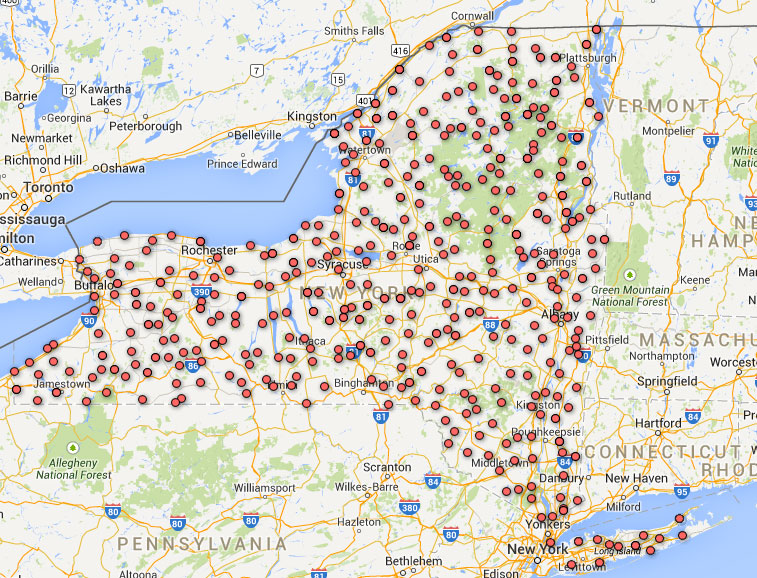
Last summer, we surveyed 400 lakes throughout New York State for starry stonewort and other green algae. Grappling hooks in hand, we traversed the state on week-long excursions, averaging 10 lakes per day. At each lake, we used the grappling hooks to gather algal specimens and also collected water-chemistry data and documented physical characteristics. There was no shortage of excitement on our journey, owing to multiple tornado warnings, many bear-sightings, and countless beautiful vistas.
We found starry stonewort in lakes across New York, from Jamestown to Potsdam, but did not find it within the boundaries of Adirondack Park. This is good news for the millions who visit the Park annually. The Adirondack region has a strong Watershed Stewardship Program, and we are partnering with this program to raise awareness about starry stonewort and the measures that can be taken—such as cleaning and fully drying boats and gear—to keep this invasive out of Adirondack lakes and ponds.
Now we are taking our grappling hooks to New England to conduct a similar survey of lakes, so stay tuned for more updates.


Interesting article—Curious to see what is found in New England ponds.
-Al Stoops
Nelson, NH