Get to Know Daffodils
Daffodils can be classified into 13 different divisions based on their anatomy, but they all share the same basic biology.
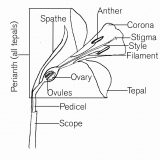
Scope, or stem – carries food, water and minerals throughout the plant, and supports the flower.
Pedicel – the stalk of a single flower on a stem with multiple blooms.
Spathe – the thin brownish-green form attached to the stem at the base of the flower. Forms a protective layer over the bud, and unwraps as the bloom opens.
Perianth and tepals – tepals, or petals, form above the ovary. All of the tepals of a daffodil are referred to collectively as the perianth.
Corona – the central structure of the flower, extending outward from the petals, is named for its crown-like shape.
Stigma – Part of the female reproductive system of the flower, the stigma is the pollen accepting organ.
Style – Part of the female reproductive system, the style connects the stigma to the ovary.
Ovary and ovules – the female part of the plant, which contains ovules. After an ovule is pollinated it becomes a seed.
Anther – the male pollen creating organ, consists of six pollen covered structures surrounding the stigma.
Filament – the supporting structure of the anthers.